Cureus, Whole-Exome Sequencing Identified a Novel DYRK1A Variant in a Patient With Intellectual Developmental Disorder, Autosomal Dominant 7
Por um escritor misterioso
Descrição
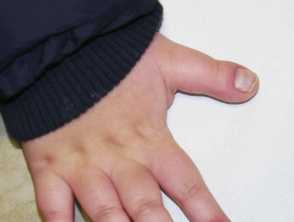
Intellectual developmental disorder, autosomal dominant 7 (MRD7; OMIM 614104) is a rare disease characterized by microcephaly, intellectual disability, speech delay, feeding difficulties, and facial dysmorphisms. This disorder is caused by pathogenic/likely pathogenic variants of the DYRK1A gene, which encodes dual-specificity tyrosine-phosphorylation-regulated kinase 1A. Here, we report a case of MRD7 that was diagnosed using Face2Gene and whole-exome sequencing (WES). A 22-year-old man presented with microcephaly, intellectual disability, slender body, long slender fingers, and facial dysmorphisms. He was previously diagnosed with Cornelia de Lange syndrome (CdLS) at four years of age. However, his CdLS clinical diagnostic score was low at 22 years of age. The Face2Gene application introduced several candidate diseases including MRD7. Finally, by utilizing WES and Sanger sequencing analysis of cloned cDNA, we identified a novel heterozygous duplication variant (c.848dup, p.(Asn283LysfsTer6)) in the DYRK1A gene, which introduces a premature stop codon. This report provides more information about the phenotypic spectrum of a young adult patient with MRD7. Face2Gene helped us introduce candidate diseases of the patient. Registering further genetically confirmed cases with MRD7 will improve the accuracy of the diagnostic recommendations in Face2Gene. Moreover, WES is a powerful tool for diagnosing rare genetic diseases, such as MRD7.
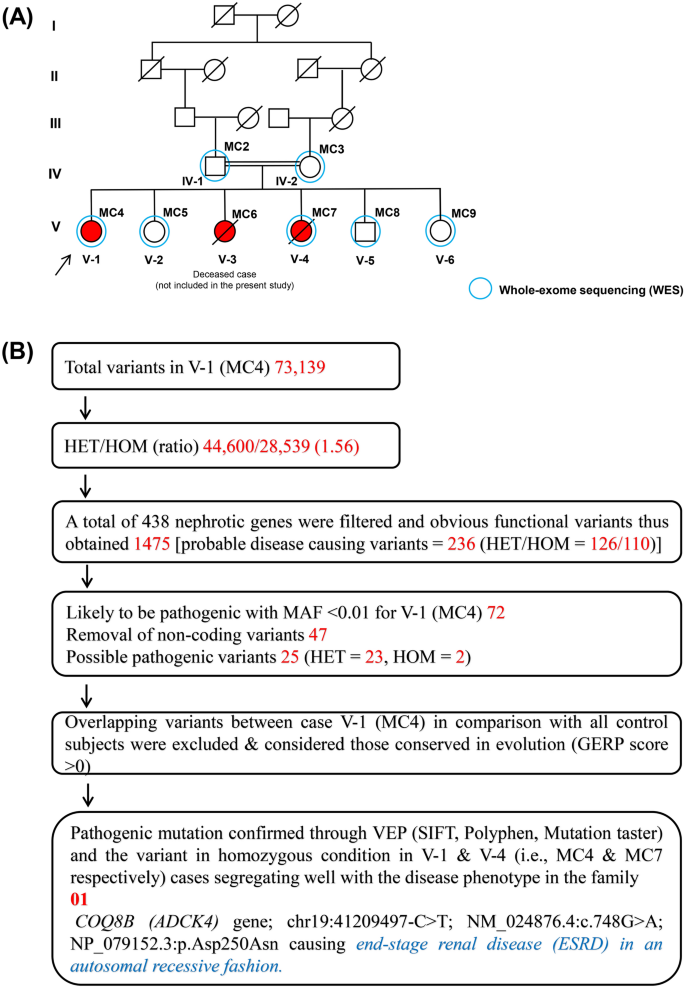
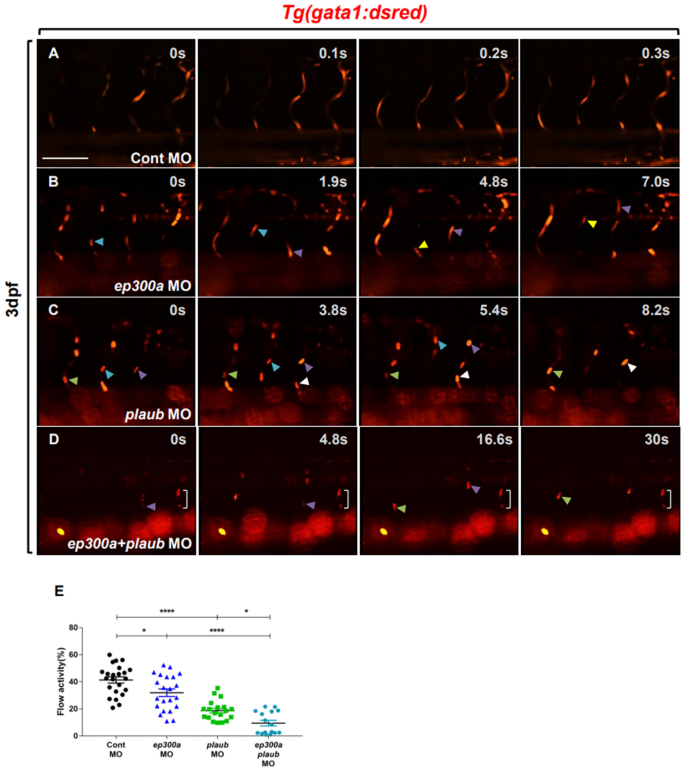
Whole-exome sequencing reveals a novel homozygous mutation in the COQ8B gene associated with nephrotic syndrome

Ten new cases further delineate the syndromic intellectual disability phenotype caused by mutations in DYRK1A. - Abstract - Europe PMC
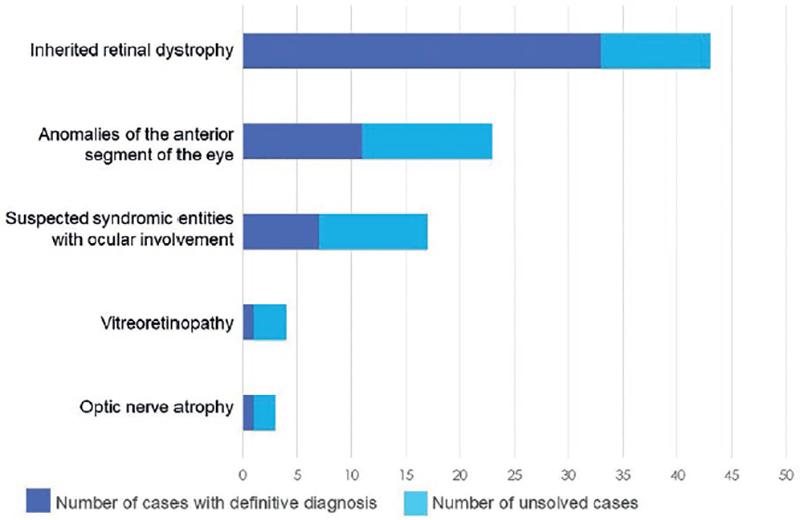
Effectiveness of Whole-Exome Sequencing for the Identification of Causal Mutations in Patients with Suspected Inherited Ocular Diseases
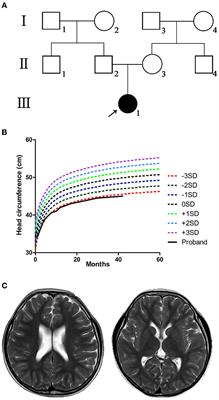
Frontiers Case report: A novel de novo deletion mutation of DYRK1A is associated with intellectual developmental disorder, autosomal dominant 7

Integrative approach to interpret DYRK1A variants, leading to a frequent neurodevelopmental disorder

Clinical whole-exome sequencing for the diagnosis of rare disorders with congenital anomalies and/or intellectual disability: substantial interest of prospective annual reanalysis - ScienceDirect

Clinical Application of Genome and Exome Sequencing as a Diagnostic Tool for Pediatric Patients: a Scoping Review of the Literature - ScienceDirect
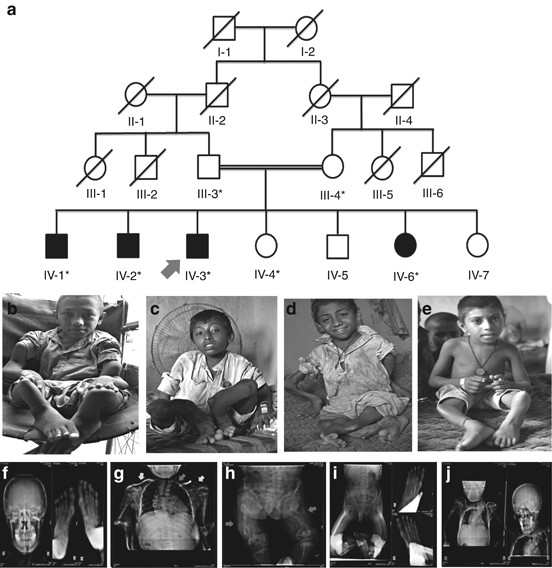
Exome sequencing reveals a novel homozygous splice site variant in the WNT1 gene underlying osteogenesis imperfecta type 3
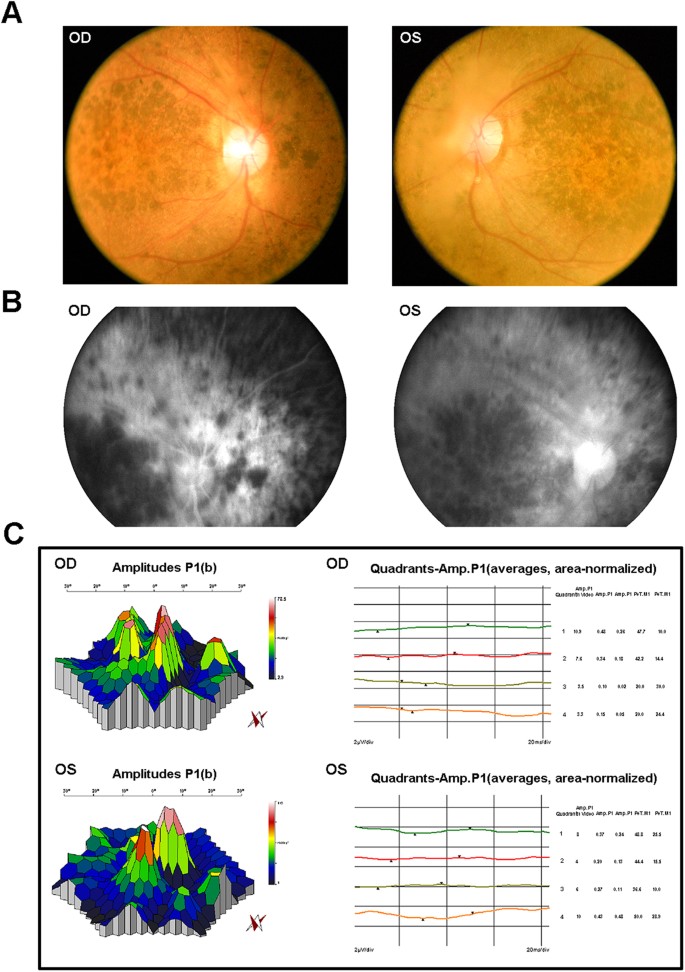
Whole exome sequencing identified novel CRB1 mutations in Chinese and Indian populations with autosomal recessive retinitis pigmentosa
de
por adulto (o preço varia de acordo com o tamanho do grupo)