Pathogens, Free Full-Text
Por um escritor misterioso
Descrição
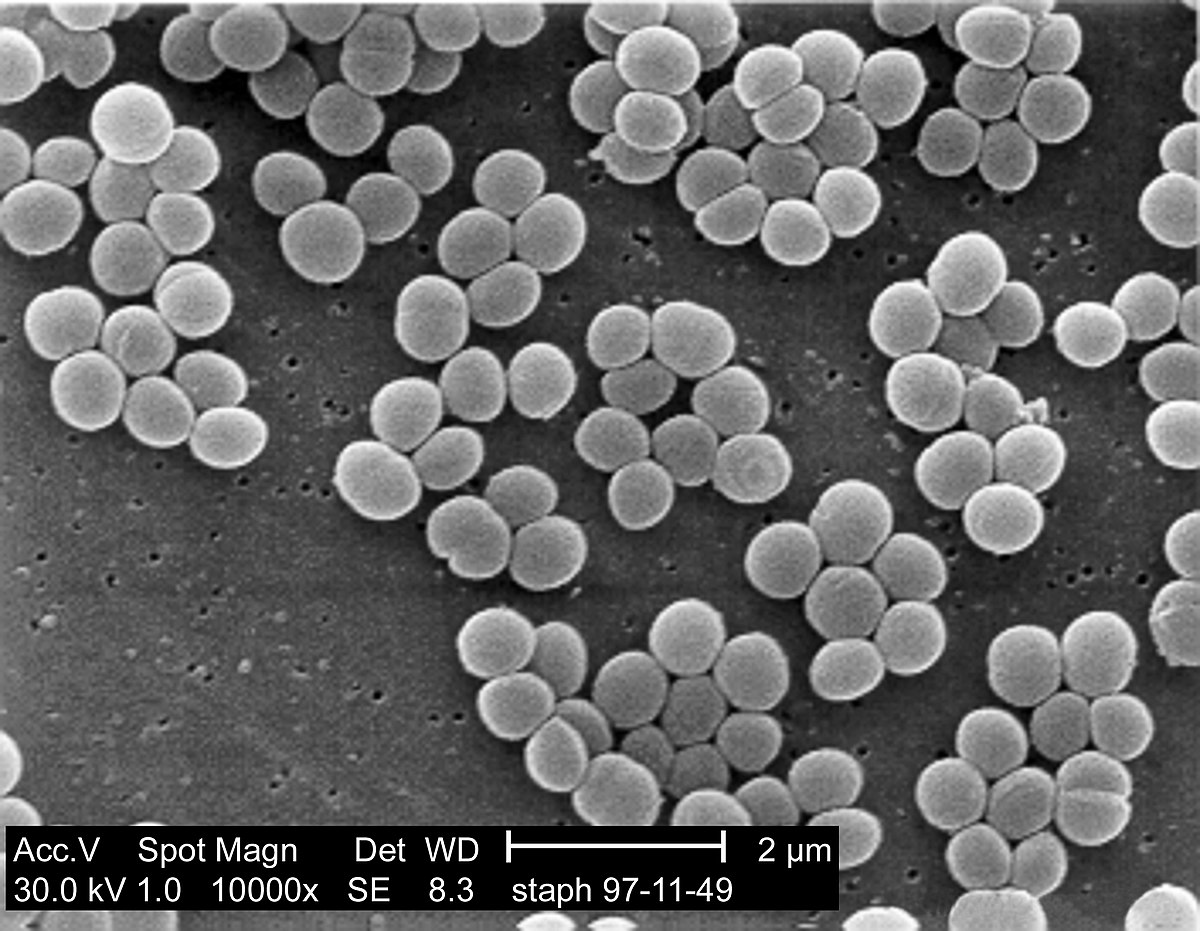
Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus) causes the vast majority of skin and soft tissue infections (SSTIs) in humans. S. aureus has become increasingly resistant to antibiotics and there is an urgent need for new strategies to tackle S. aureus infections. Vaccines offer a potential solution to this epidemic of antimicrobial resistance. However, the development of next generation efficacious anti-S. aureus vaccines necessitates a greater understanding of the protective immune response against S. aureus infection. In particular, it will be important to ascertain if distinct immune mechanisms are required to confer protection at distinct anatomical sites. Recent discoveries have highlighted that interleukin-17-producing T cells play a particularly important role in the immune response to S. aureus skin infection and suggest that vaccine strategies to specifically target these types of T cells may be beneficial in the treatment of S. aureus SSTIs. S. aureus expresses a large number of cell wall-anchored (CWA) proteins, which are covalently attached to the cell wall peptidoglycan. The virulence potential of many CWA proteins has been demonstrated in infection models; however, there is a paucity of information regarding their roles during SSTIs. In this review, we highlight potential candidate antigens for vaccines targeted at protection against SSTIs.

Cellular Microbiology - Wiley Online Library

The Disease Triangle: Fundamental Concept for Disease Management - Nursery and Flower Grower - ANR Blogs

What is Required If Your Athletic Facility Needs a Blood-Borne Pathogens Plan?: Journal of Physical Education, Recreation & Dance: Vol 71, No 6

ThinkLite Natick MA

Identification of Antibiotic Resistance in ESKAPE Pathogens through Plasmonic Nanosensors and Machine Learning
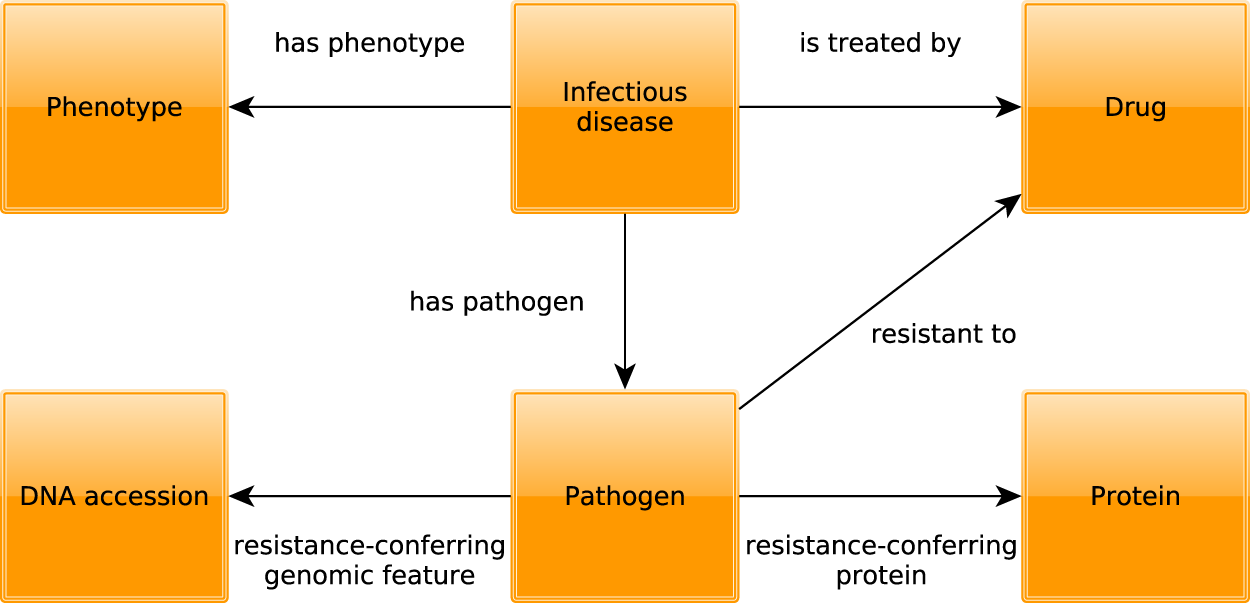
PathoPhenoDB, linking human pathogens to their phenotypes in support of infectious disease research

Global burden of bacterial antimicrobial resistance in 2019: a systematic analysis - The Lancet

Plant pathology - Wikipedia
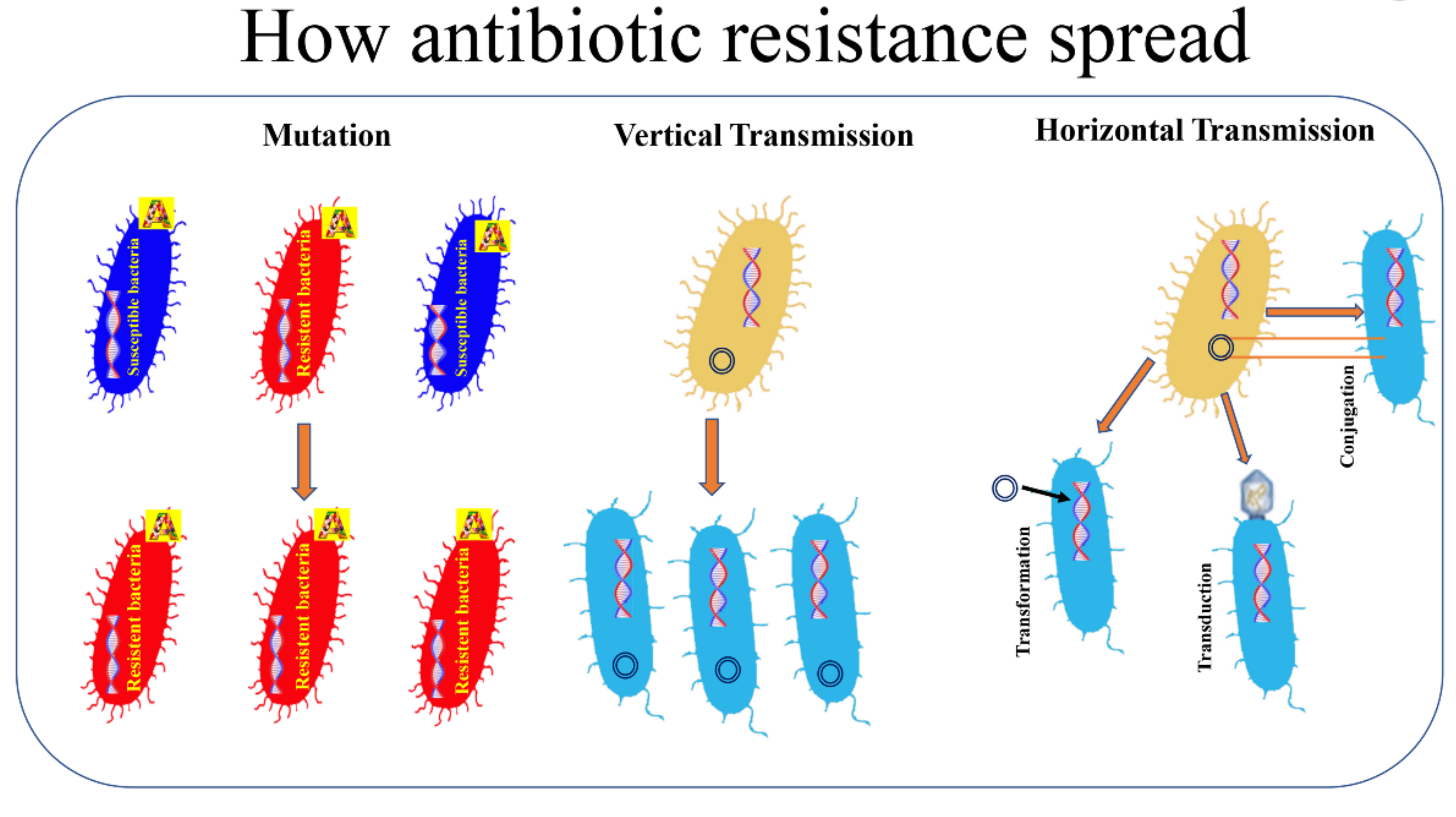
Pathogens, Free Full-Text

Pathogenic bacteria - Wikipedia

Solved 1. What is epithelia, what is an example of
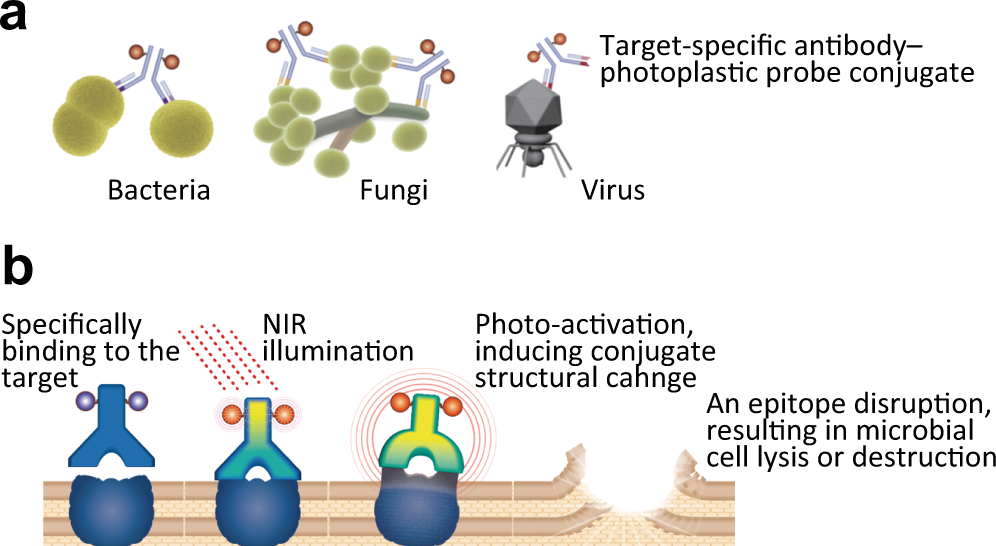
Antimicrobial strategy for targeted elimination of different microbes, including bacterial, fungal and viral pathogens
Lung lysophospholipase activity in specific-pathogen-free rats infected with Pasteurella pneumotropica or Mycoplasma pulmonis. - Abstract - Europe PMC
de
por adulto (o preço varia de acordo com o tamanho do grupo)