Understanding SARS-CoV-2-Mediated Inflammatory Responses: From
Por um escritor misterioso
Descrição
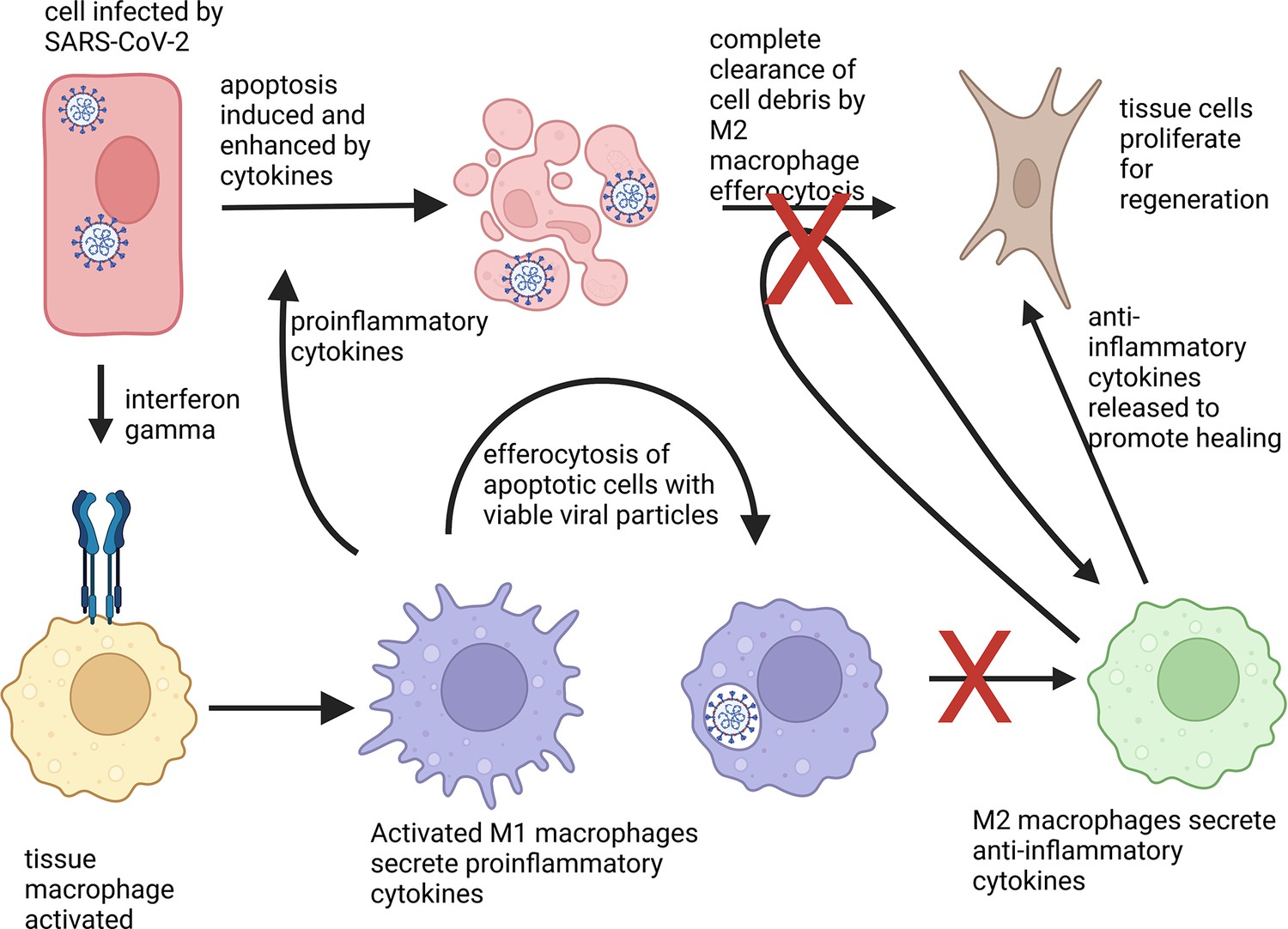
Currently there is no effective antiviral therapy for SARS-CoV-2 infection, which frequently leads to fatal inflammatory responses and acute lung injury. Here, we discuss the various mechanisms of SARS-CoV-mediated inflammation. We also assume that SARS-CoV-2 likely shares similar inflammatory responses. Potential therapeutic tools to reduce SARS-CoV-2-induced inflammatory responses include various methods to block FcR activation. In the absence of a proven clinical FcR blocker, the use of intravenous immunoglobulin to block FcR activation may be a viable option for the urgent treatment of pulmonary inflammation to prevent severe lung injury. Such treatment may also be combined with systemic anti-inflammatory drugs or corticosteroids. However, these strategies, as proposed here, remain to be clinically tested for effectiveness.

Mechanisms of SARS-CoV-2 Transmission and Pathogenesis: Trends in Immunology

Involvement of autophagy in lymphocyte-mediated inflammation during
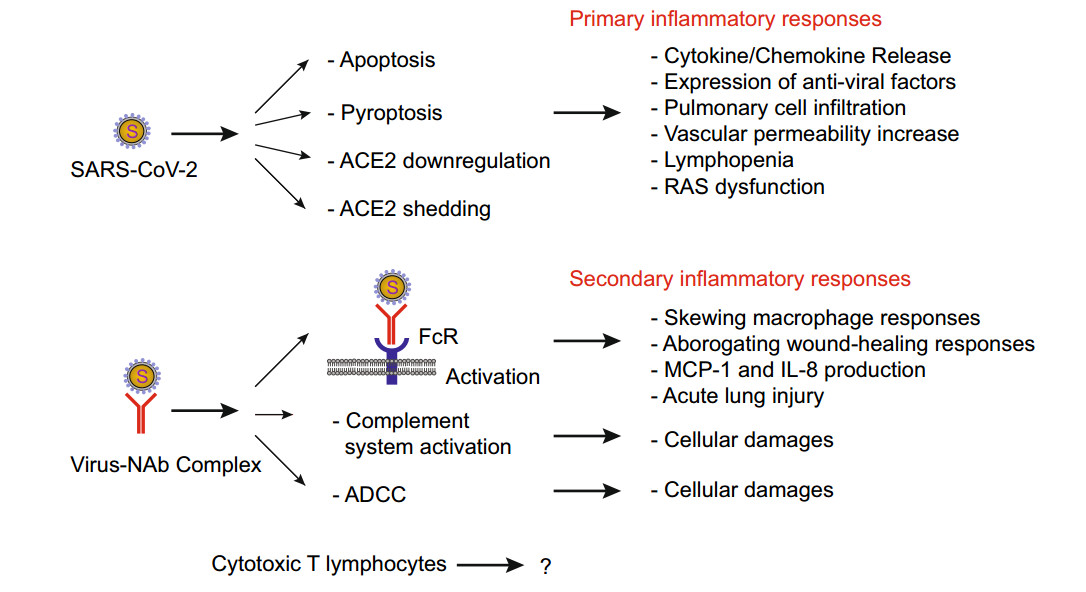
Understanding SARS-CoV-2-Mediated Inflammatory Responses: From Mechanisms to Potential Therapeutic Tools
Lab-Grown Mini-Lungs Mimic the Real Thing – Right Down to Covid Infection

Post-acute sequelae of COVID-19: understanding and addressing the burden of multisystem manifestations - The Lancet Respiratory Medicine
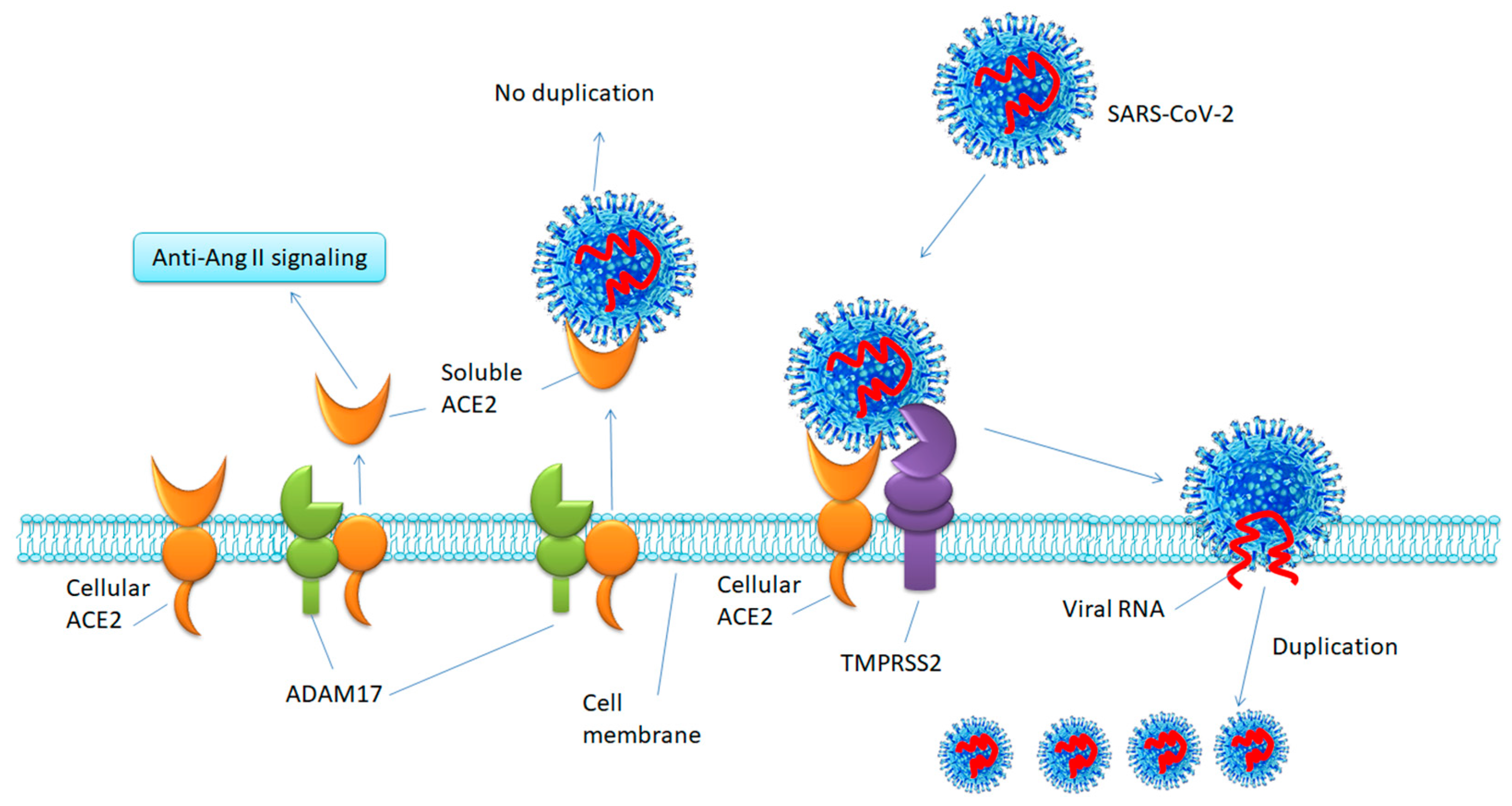
Viruses, Free Full-Text

Tobacco product use and the risks of SARS-CoV-2 infection and COVID-19: current understanding and recommendations for future research - The Lancet Respiratory Medicine

Soluble ACE2-mediated cell entry of SARS-CoV-2 via interaction with proteins related to the renin-angiotensin system - ScienceDirect
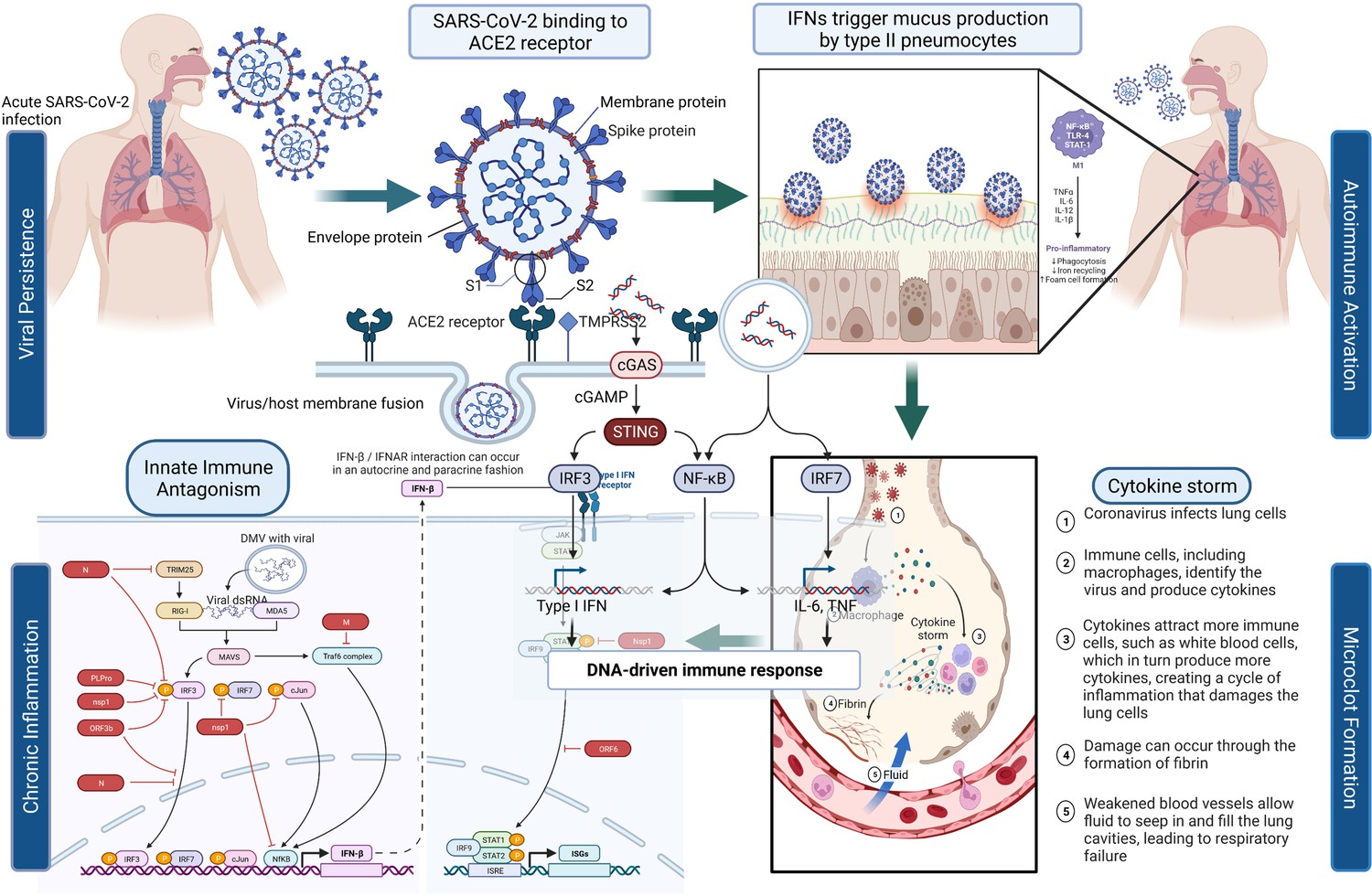
Pathogenic mechanisms of post-acute sequelae of SARS-CoV-2 infection (PASC)

Full article: Short- and potential long-term adverse health outcomes of COVID-19: a rapid review

Inflammatory pathways in COVID‐19: Mechanism and therapeutic interventions - Jiang - 2022 - MedComm - Wiley Online Library

Does infection with or vaccination against SARS-CoV-2 lead to lasting immunity? - The Lancet Respiratory Medicine
COVID-19: Locked in a pro-inflammatory state

Toll-Like Receptor 4-Dependent Platelet-Related Thrombosis in SARS-CoV-2 Infection
de
por adulto (o preço varia de acordo com o tamanho do grupo)







