PDF] Patent Ductus Arteriousus Device Closure in an Infant with Rubinstein–Taybi Syndrome
Por um escritor misterioso
Descrição
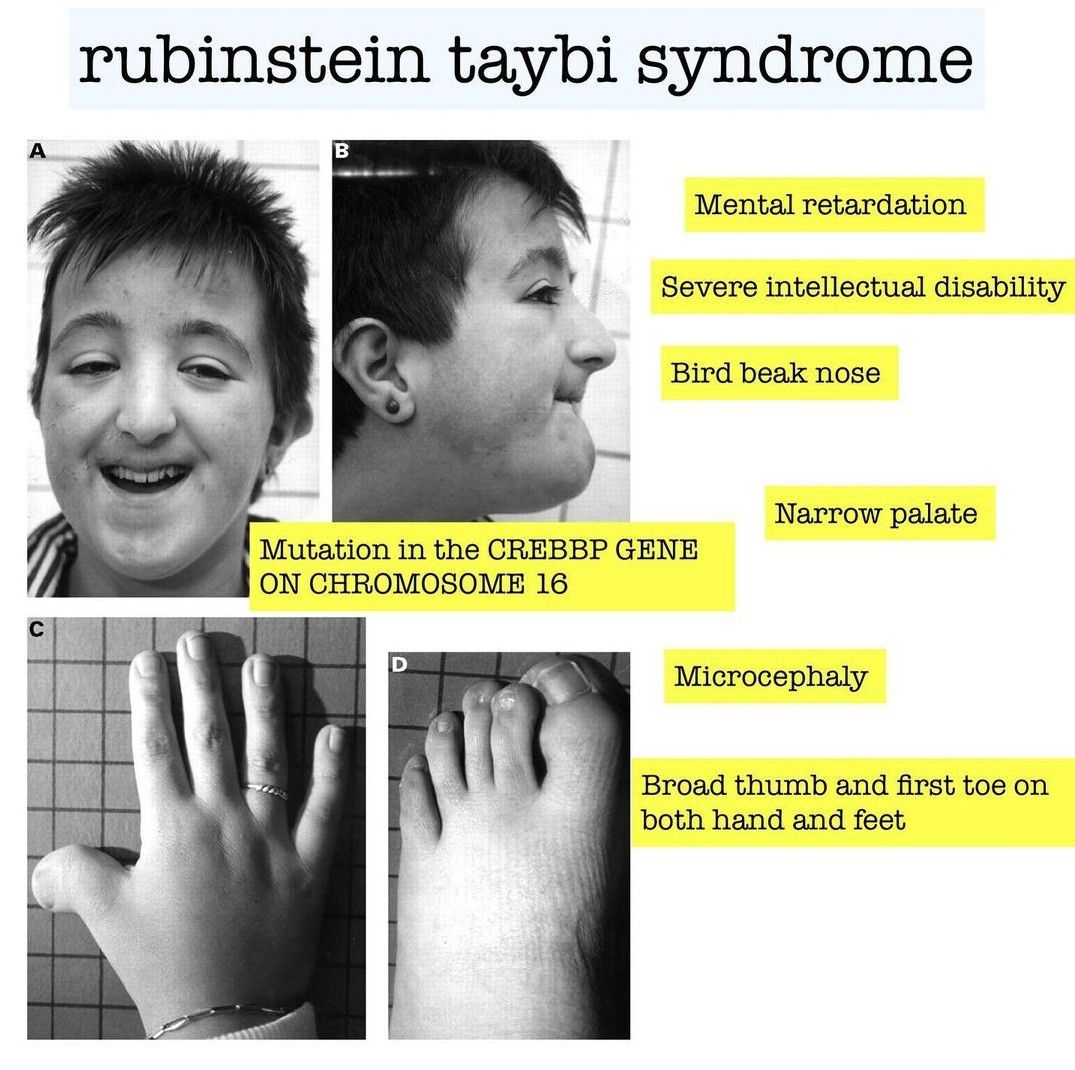
A typical six-month-old girl with Rubinstein–Taybi syndrome was presented with typical facial changes including downward-sloping palpebral fissures, prominent forehead, hypertelorism, limited mouth opening, large beaked nose, and high arched palate. Rubinstein–Taybi syndrome (RTS) was first described by Michail et al[1] and subsequently by Rubinstein and Taybi[2]. We present a typical six-month-old girl with RTS. Her mother had ovarian cancer and polyhydramnios during the pregnancy. Parents are closely related. There were frequent respiratory infections resulting in two hospital admissions. Physical examination revealed typical facial changes including downward-sloping palpebral fissures, prominent forehead, hypertelorism, limited mouth opening, large beaked nose, and high arched palate (Fig. 1). A history of increased tearing was compatible with nasolacrimal duct obstruction. Other features include general hypotonia with delayed developmental milestones, short and broad thumbs and toes (Fig. 1). Chest x-ray showed cardiomegaly (Fig. 2). She had normal karyotype.
![PDF] Patent Ductus Arteriousus Device Closure in an Infant with Rubinstein–Taybi Syndrome](https://d3i71xaburhd42.cloudfront.net/23617ae5de57698a16f51313ff821d46e487f2c2/4-Table2-1.png)
PDF] Percutaneous Patent Ductus Arteriosus (PDA) Closure in Very Preterm Infants: Feasibility and Complications
![PDF] Patent Ductus Arteriousus Device Closure in an Infant with Rubinstein–Taybi Syndrome](https://d3i71xaburhd42.cloudfront.net/23617ae5de57698a16f51313ff821d46e487f2c2/2-Figure1-1.png)
PDF] Percutaneous Patent Ductus Arteriosus (PDA) Closure in Very Preterm Infants: Feasibility and Complications
![PDF] Patent Ductus Arteriousus Device Closure in an Infant with Rubinstein–Taybi Syndrome](https://i1.rgstatic.net/ii/profile.image/926912121675782-1598004479904_Q64/Ehsan-Aghaei-Moghadam.jpg)
PDF) Patent Ductus Arteriousus Device Closure in an Infant with Rubinstein–Taybi Syndrome
![PDF] Patent Ductus Arteriousus Device Closure in an Infant with Rubinstein–Taybi Syndrome](https://d3i71xaburhd42.cloudfront.net/23617ae5de57698a16f51313ff821d46e487f2c2/7-Table7-1.png)
PDF] Percutaneous Patent Ductus Arteriosus (PDA) Closure in Very Preterm Infants: Feasibility and Complications
![PDF] Patent Ductus Arteriousus Device Closure in an Infant with Rubinstein–Taybi Syndrome](https://media.springernature.com/m685/springer-static/image/art%3A10.1038%2Fs41372-019-0513-8/MediaObjects/41372_2019_513_Fig2_HTML.png)
Comparison of 'post-patent ductus arteriosus ligation syndrome' in premature infants after surgical ligation vs. percutaneous closure
![PDF] Patent Ductus Arteriousus Device Closure in an Infant with Rubinstein–Taybi Syndrome](https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/cms/asset/4ce6779d-2330-4abf-bb6e-2cd14e352bf1/jocs15171-fig-0001-m.jpg)
Bedside surgical ligation of the patent ductus arteriosus in very‐low‐birth‐weight premature infants: Limited upper ministernotomy as an alternative approach - Akyuz - 2021 - Journal of Cardiac Surgery - Wiley Online Library
![PDF] Patent Ductus Arteriousus Device Closure in an Infant with Rubinstein–Taybi Syndrome](https://ars.els-cdn.com/content/image/1-s2.0-S1875957222002741-gr1.jpg)
Clinical outcomes of different patent ductus arteriosus treatment in preterm infants born between 28 and 32 weeks in Taiwan - ScienceDirect
![PDF] Patent Ductus Arteriousus Device Closure in an Infant with Rubinstein–Taybi Syndrome](https://ars.els-cdn.com/content/image/1-s2.0-S1058981319301821-gr3.jpg)
Transcatheter closure of patent ductus arteriosus in a tiniest baby – 510 grams - ScienceDirect
![PDF] Patent Ductus Arteriousus Device Closure in an Infant with Rubinstein–Taybi Syndrome](https://www.researchgate.net/publication/262940679/figure/fig1/AS:601613563600903@1520447259122/a-chest-X-ray-showing-mild-cardiomegaly-with-increased-pulmonary-vascular-marking-b_Q320.jpg)
PDF) Patent Ductus Arteriousus Device Closure in an Infant with Rubinstein–Taybi Syndrome
![PDF] Patent Ductus Arteriousus Device Closure in an Infant with Rubinstein–Taybi Syndrome](https://osmose-it.s3.amazonaws.com/9W-42F6qQx_fyo8uFIzJsZ-_TTSkhjhP/assets/page-6.svg)
Patent ductus arteriosus: Video, Anatomy & Definition
![PDF] Patent Ductus Arteriousus Device Closure in an Infant with Rubinstein–Taybi Syndrome](https://f6publishing.blob.core.windows.net/a7a9dd9c-137e-4223-8b63-2a1ab9b60b69/WJC-14-54-g001.png)
Anesthetic management of a child with Cornelia de Lange Syndrome undergoing open heart surgery: A case report
![PDF] Patent Ductus Arteriousus Device Closure in an Infant with Rubinstein–Taybi Syndrome](https://ars.els-cdn.com/content/image/1-s2.0-S1875213610001555-gr3.jpg)
The ductus arteriosus: Physiology, regulation, and functional and congenital anomalies - ScienceDirect
de
por adulto (o preço varia de acordo com o tamanho do grupo)

:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/pediatrician-487474340-3f639b1d87444d45b10ba75b77446051.jpg)




:format(jpeg)/cdn.vox-cdn.com/photo_images/2350761/GYI0064179976.jpg)